#
What is a Tensor ?
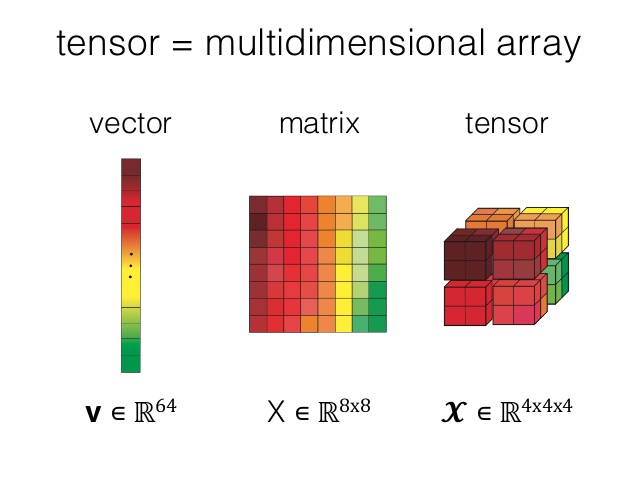
A tensor is a multi-dimensional array used to store data in a structured way.
For example, an image can be represented as a tensor with the shape [3, 128, 128], where [color_channels, height, width] indicates that the image has 3 color channels (red, green, blue), a height of 128 pixels, and a width of 128 pixels.
Similarly, audio data can be represented as a tensor where each element corresponds to a numerical value representing an audio sample. For example, a mono audio signal of 1 second at a 16 kHz sampling rate could be represented as a tensor of shape [16000], indicating 16,000 samples. This concept can be extended to various other types of data.
Quick recap:
- 0-D Tensor (Scalar): A single number. Example:
5. - 1-D Tensor (Vector): A list of numbers. Example:
[1, 2, 3]. - 2-D Tensor (Matrix): A grid of numbers. Example:
[[1, 2], [3, 4]]. - 3-D Tensor and Higher: A stack of matrices or more complex structures. Example:
[[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]].
To understand how tensors represent data, watch this video: What's a Tensor?
